HTB Cyber Apocalypse CTF: Android-in-the-Middle, Jenny From the Block, and How the Columns have Turned

Intro
We’re going to knock out three in one here as the other 1-star crypto challenges in this CTF weren’t incredibly complicated, and I can’t really justify 3 separate posts for each of them.
Android in the Middle was a cute little play on the Diffie-Hellman Man-in-the-middle attack where you could submit your own public key in the exchange and then need to provide an encrypted string, but you don’t have any other information aside from the public key of the server. So, we can use math to submit a public key of 1 so we can bootstrap the encryption ourselves to get the flag.
Jenny from the Block was a super simple custom block cipher that suffered from knowing a plaintext-ciphertext combination, which allows you to bruteforce the initial key, which you can then use to decrypt the following blocks as the encryption algorithm is super easy to reverse.
How the Columns Have Turned was an easy challenge that I just spent way too long on because I didn’t read closely enough. It features an ineffective PRNG to generate a key for a Columnar Cipher that’s been modified to operate on the transpose of the initial set of blocks. However, this isn’t that hard to reverse.
Android-in-the-Middle
Description
Years have passed since Miyuki rescued you from the graveyard. When Virgil tells you that he needs your help with something he found there, desperate thoughts about your father and the disabilities you developed due to the disposal process come to mind. The device looks like an advanced GPS with AI capabilities. Riddled with questions about the past, you are pessimistic that you could be of any value. After hours of fiddling and observing the power traces of this strange device, you and Virgil manage to connect to the debugging interface and write an interpreter to control the signals. The protocol looks familiar to you. Your father always talked about implementing this scheme in devices for security reasons. Could it have been him?
Challenge
We’re given source code to a live instance.
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
import hashlib
import random
import socketserver
import signal
FLAG = "HTB{--REDACTED--}"
DEBUG_MSG = "DEBUG MSG - "
p = 0x509efab16c5e2772fa00fc180766b6e62c09bdbd65637793c70b6094f6a7bb8189172685d2bddf87564fe2a6bc596ce28867fd7bbc300fd241b8e3348df6a0b076a0b438824517e0a87c38946fa69511f4201505fca11bc08f257e7a4bb009b4f16b34b3c15ec63c55a9dac306f4daa6f4e8b31ae700eba47766d0d907e2b9633a957f19398151111a879563cbe719ddb4a4078dd4ba42ebbf15203d75a4ed3dcd126cb86937222d2ee8bddc973df44435f3f9335f062b7b68c3da300e88bf1013847af1203402a3147b6f7ddab422d29d56fc7dcb8ad7297b04ccc52f7bc5fdd90bf9e36d01902e0e16aa4c387294c1605c6859b40dad12ae28fdfd3250a2e9
g = 2
def decrypt(encrypted, shared_secret):
key = hashlib.md5(long_to_bytes(shared_secret)).digest()
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB)
message = cipher.decrypt(encrypted)
return message
def main(s):
sendMessage(s, DEBUG_MSG + "Generating The Global DH Parameters\n")
sendMessage(s, DEBUG_MSG + f"g = {g}, p = {p}\n")
sendMessage(s, DEBUG_MSG + "Calculation Complete\n\n")
sendMessage(s, DEBUG_MSG + "Generating The Public Key of CPU...\n")
c = random.randrange(2, p - 1)
C = pow(g, c, p)
sendMessage(s, DEBUG_MSG + "Calculation Complete\n")
sendMessage(s, DEBUG_MSG + "Public Key is: ???\n\n")
M = recieveMessage(s, "Enter The Public Key of The Memory: ")
try:
M = int(M)
except:
sendMessage(s, DEBUG_MSG + "Unexpected Error Occured\n")
exit()
sendMessage(s, "\n" + DEBUG_MSG + "The CPU Calculates The Shared Secret\n")
shared_secret = pow(M, c, p)
sendMessage(s, DEBUG_MSG + "Calculation Complete\n\n")
encrypted_sequence = recieveMessage(
s, "Enter The Encrypted Initialization Sequence: ")
try:
encrypted_sequence = bytes.fromhex(encrypted_sequence)
assert len(encrypted_sequence) % 16 == 0
except:
sendMessage(s, DEBUG_MSG + "Unexpected Error Occured\n")
exit()
sequence = decrypt(encrypted_sequence, shared_secret)
if sequence == b"Initialization Sequence - Code 0":
sendMessage(s, "\n" + DEBUG_MSG +
"Reseting The Protocol With The New Shared Key\n")
sendMessage(s, DEBUG_MSG + f"{FLAG}")
else:
exit()
The server will generate a public key for itself using a secure prime and generator value and tell us what it is. We’re then prompted with a field to submit our own public key, and then are expected to submit an encrypted string to get the flag back.
This challenge is making use of the Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange, which is a public key protocol commonly used to bootstrap symmetric encryption. I won’t go into the details here, but I’ll steal a quick slide from my Encryption class.
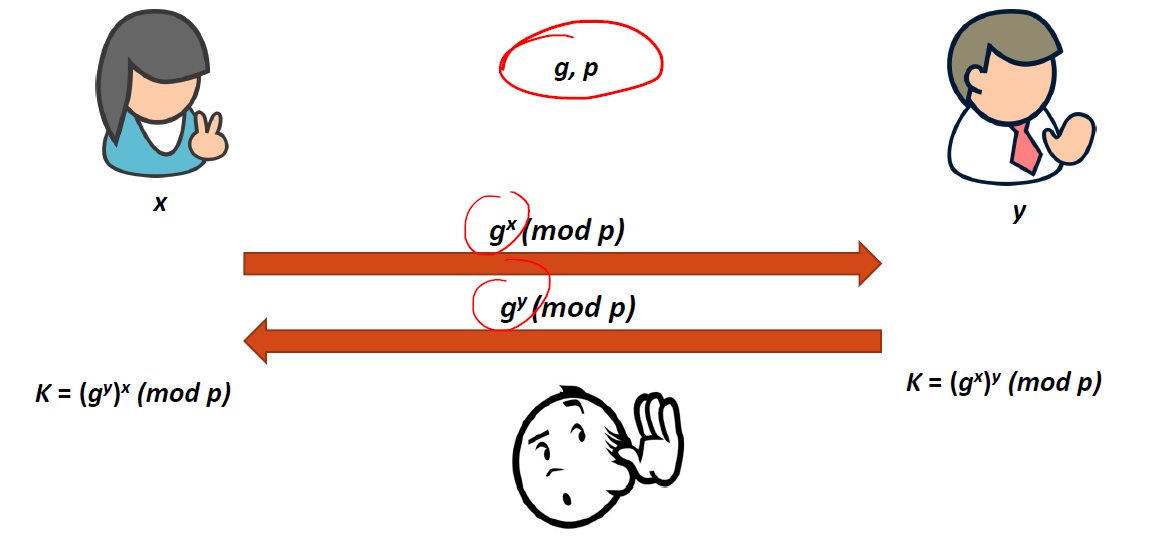
Here, we select a public prime p, and a generator for that mod-p group, g. Alice selects a secret value x, and Bob selects a secret value y (both are within the field). They both exchange exponentiated values, which are their public keys, and then each raises the other’s public key to the power of their own secret. Notice that x and y are never shared across the channel where an eavesdropper could be listening. This is secure because of what’s known as the Discrete Logarithm Problem. The gist of it is that you can’t just take the log of the value you get, because the mod p wraps it around such that it’s seemingly random.
Now that we understand Diffie-Hellman from a high level, how do we find the secret if Alice never gives us her public key? Well, it’s pretty simple. Just say your public key is 1.
\[\begin{aligned} & K \equiv 1 \equiv 1^x \pmod p \end{aligned}\]
1 to any power is 1, so we can then just use the value of 1 to bootstrap our AES encryption as shown in the challenge.
Solution
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
import hashlib
context.log_level = 'info'
r = remote('206.189.126.144', 30923)
# Hardcoded
p = 0x509efab16c5e2772fa00fc180766b6e62c09bdbd65637793c70b6094f6a7bb8189172685d2bddf87564fe2a6bc596ce28867fd7bbc300fd241b8e3348df6a0b076a0b438824517e0a87c38946fa69511f4201505fca11bc08f257e7a4bb009b4f16b34b3c15ec63c55a9dac306f4daa6f4e8b31ae700eba47766d0d907e2b9633a957f19398151111a879563cbe719ddb4a4078dd4ba42ebbf15203d75a4ed3dcd126cb86937222d2ee8bddc973df44435f3f9335f062b7b68c3da300e88bf1013847af1203402a3147b6f7ddab422d29d56fc7dcb8ad7297b04ccc52f7bc5fdd90bf9e36d01902e0e16aa4c387294c1605c6859b40dad12ae28fdfd3250a2e9
g = 2
message = b"Initialization Sequence - Code 0"
def encrypt(message, shared_secret):
key = hashlib.md5(long_to_bytes(shared_secret)).digest()
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB)
message = cipher.encrypt(message)
return message
r.sendlineafter('Enter The Public Key of The Memory:', '1')
r.sendlineafter('Enter The Encrypted Initialization Sequence:', encrypt(message, 1).hex())
flag = r.recvall()
success(flag)
Running it, we get the flag:
kali@transistor:~/ctf/cyber_apocalypse/crypto/crypto_android-in-the-middle$ python3 solve.py
[+] Opening connection to 206.189.126.144 on port 30923: Done
[*] Closed connection to 206.189.126.144 port 30923
/home/kali/.local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pwnlib/log.py:346: BytesWarning: Bytes is not text; assuming ASCII, no guarantees. See https://docs.pwntools.com/#bytes
self._log(logging.INFO, message, args, kwargs, 'success')
[+]
DEBUG MSG - Reseting The Protocol With The New Shared Key
DEBUG MSG - HTB{7h15_p2070c0l_15_pr0tec73d_8y_D@nb3er_c0pyr1gh7_1aws}
Jenny From the Block
Description
Intrigued by the fact that you have found something your father made, and with much confidence that you can be useful to the team, you rush excitedly to integrate “Jenny” into the spaceship’s main operating system. For weeks, everything went smoothly, until you ran into a meteor storm. Having little to no data of training, the AI is now malfunctioning. Ulysses freaks out because he can no longer control the spaceship due to the AI overriding his manual commands. Big banging noises terrify your crew members. Everything is shaking. It’s time to act. Do you think you can temporarily shut down “Jenny” until she becomes more sophisticated?
Challenge
We’re given more source code to an instance.
from hashlib import sha256
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad, unpad
import signal
import subprocess
import socketserver
import os
allowed_commands = [b'whoami', b'ls', b'cat secret.txt', b'pwd']
BLOCK_SIZE = 32
def encrypt_block(block, secret):
enc_block = b''
for i in range(BLOCK_SIZE):
val = (block[i]+secret[i]) % 256
enc_block += bytes([val])
return enc_block
def encrypt(msg, password):
h = sha256(password).digest()
if len(msg) % BLOCK_SIZE != 0:
msg = pad(msg, BLOCK_SIZE)
blocks = [msg[i:i+BLOCK_SIZE] for i in range(0, len(msg), BLOCK_SIZE)]
ct = b''
for block in blocks:
enc_block = encrypt_block(block, h)
h = sha256(enc_block + block).digest()
ct += enc_block
return ct.hex()
def run_command(cmd):
if cmd in allowed_commands:
try:
resp = subprocess.run(
cmd.decode().split(' '), capture_output=True)
output = resp.stdout
return output
except:
return b'Something went wrong!\n'
else:
return b'Invalid command!\n'
def challenge(req):
req.sendall(b'This is Jenny! I am the heart and soul of this spaceship.\n' +
b'Welcome to the debug terminal. For security purposes I will encrypt any responses.')
while True:
req.sendall(b'\n> ')
command = req.recv(4096).strip()
output = run_command(command)
response = b'Command executed: ' + command + b'\n' + output
password = os.urandom(32)
ct = encrypt(response, password)
req.sendall(ct.encode())
The function of the instance isn’t terribly complicated, run one of four predetermined commands, get the output (concatenated with additional strings) back but encrypted. Interestingly, there isn’t any common block cipher in use, in fact, it’s custom. Luckily, the encryption function is fairly simple.
We begin by breaking up our message into 32 byte blocks. The initial password is the SHA256 hash a random 32 bytes. For each block in our set of blocks, we will encrypt the block by adding the bytes moduluo 256. We then set the new password to be the SHA256 sum of the encrypted block concatenated with the plaintext block. More visually:
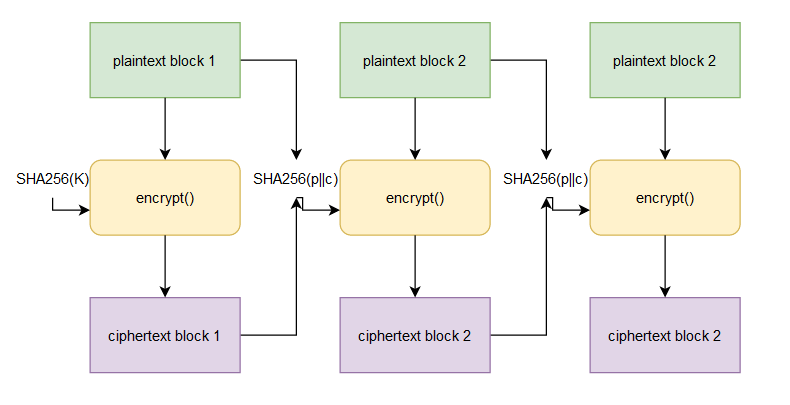
We can actually recover the initial key very easily. Recall that our message is command is being preppended by “Command executed: “. Turns out, the length of “Command executed: cat secret.txt” is exactly 32 bytes. So, we can bruteforce the initial key because the algorithm is pretty fast, and from there, we can run the algorithm as shown in the source code to recover the rest of the plaintext keys. The modulus operation can be reversed by simply subtracting instead of adding, so we’re good to go!
Solution
#!/usr/bin/python3
from pwn import *
from hashlib import sha256
BLOCK_SIZE = 32
def decrypt_block(block, secret):
dec_block = b''
for i in range(BLOCK_SIZE):
val = (block[i]-secret[i]) % 256
dec_block += bytes([val])
return dec_block
r = remote('157.245.40.139',30855)
message = b'Command executed: cat secret.txt'
r.sendlineafter('>', 'cat secret.txt')
ct = r.recvlineS().strip()
blocks = [ct[i:i+64] for i in range(0, len(ct), 64)]
ref = bytes.fromhex(blocks[0])
init_key = b''
p = log.progress('brute forcing initial key...')
for i in range(BLOCK_SIZE):
for guess in range(256):
val = (message[i]+guess) % 256
p.status(f'val: {val}\nref: {ref[i]}\nrec: {init_key}')
if val == ref[i]:
init_key += bytes([guess])
info(f'init_key: {init_key.hex()}')
h = init_key
plaintext = b''
for block in blocks:
block = bytes.fromhex(block)
dec_block = decrypt_block(block, h)
h = sha256(block + dec_block).digest()
plaintext += dec_block
success(plaintext.decode('utf-8'))
The first half of this code simply gets the output of cat secret.txt and bruteforces the first block by running the encryption calculation on each byte until it lines up. Then, we simply iterate over the blocks we recieve, subtract the bytes modulo 256, set up our new key, and we’ve reversed the encryption. Running the script:
kali@transistor:~/ctf/cyber_apocalypse/crypto/crypto_jenny_from_the_block$ python3 solve.py
[+] Opening connection to 206.189.126.144 on port 31613: Done
res = self.recvuntil(delim, timeout=timeout)
[◣] brute forcing initial key...: val: 115
ref: 201
rec: b'"\x14;\xf3\xb0{G\x9fd+\x14\xcbz\xf9Y\x94)\x1a+l\xe6\x12\xeb\xc4\t\x17\xf9\xa40\xabwU'
[*] init_key: 22143bf3b07b479f642b14cb7af95994291a2b6ce612ebc40917f9a430ab7755
[+] Command executed: cat secret.txt
In case Jenny malfunctions say the following phrase: Melt My Eyez, See Your Future
The AI system will shutdown and you will gain complete control of the spaceship.
- Danbeer S.A.
HTB{b451c_b10ck_c1ph3r_15_w34k!!!}
\x07\x07\x07\x07[*] Closed connection to 206.189.126.144 port 31613
Note the weird \x07’s at the end. This is because the plaintext was padded, meaning we added bytes at the end, to make sure it hit a multiple of 32. While it wasn’t absolutely necessary here, other algorithms might need it because they’re programmed to use all of bits in the block in a way that can’t really adapt to different lengths.
How the Columns Have Turned
Description
A day before the memorial of the Dying Sun, Miyuki began talking about Broider, a death squad commander and a friend of Paulie’s capturer. He would be a party guest at Viryr’s palace. After examining a lot of different scenarios, Miyuki came up with a plan in which Paulie would lure Broider to a secluded location so the group could capture him. Following the plan, a wild chase had just begun when the two looked each other in the eye. After an extremely risky maneuver, Paulie outwitted Broider and led him into an alley in Vinyr’s undercity. The plan was a success. Your squad had managed to capture Broider and bring him back to the ship. After hours of interrogation by Ulysses, he revealed the final key to a series of encrypted messages. Can you find a way to decrypt the others? The flag consists entirely of uppercase characters and has the form HTB{SOMETHINGHERE}. You still have to add the {} yourself.
Challenge
There was no instance for this challenge. We were given the encryption script, a dialog.txt, and encrypted_messages.txt.
import os
with open('super_secret_messages.txt', 'r') as f:
SUPER_SECRET_MESSAGES = [msg.strip() for msg in f.readlines()]
def deriveKey(key):
derived_key = []
for i, char in enumerate(key):
previous_letters = key[:i]
new_number = 1
for j, previous_char in enumerate(previous_letters):
if previous_char > char:
derived_key[j] += 1
else:
new_number += 1
derived_key.append(new_number)
return derived_key
def transpose(array):
return [row for row in map(list, zip(*array))]
def flatten(array):
return "".join([i for sub in array for i in sub])
def twistedColumnarEncrypt(pt, key):
derived_key = deriveKey(key)
width = len(key)
blocks = [pt[i:i + width] for i in range(0, len(pt), width)]
blocks = transpose(blocks)
ct = [blocks[derived_key.index(i + 1)][::-1] for i in range(width)]
ct = flatten(ct)
return ct
class PRNG:
def __init__(self, seed):
self.p = 0x2ea250216d705
self.a = self.p
self.b = int.from_bytes(os.urandom(16), 'big')
self.rn = seed
def next(self):
self.rn = ((self.a * self.rn) + self.b) % self.p
return self.rn
def main():
seed = int.from_bytes(os.urandom(16), 'big')
rng = PRNG(seed)
cts = ""
for message in SUPER_SECRET_MESSAGES:
key = str(rng.next())
ct = twistedColumnarEncrypt(message, key)
cts += ct + "\n"
with open('encrypted_messages.txt', 'w') as f:
f.write(cts)
dialog = "Miyuki says:\n"
dialog += "Klaus it's your time to sign!\n"
dialog += "All we have is the last key of this wierd encryption scheme.\n"
dialog += "Please do your magic, we need to gather more information if we want to defeat Draeger.\n"
dialog += f"The key is: {str(key)}\n"
with open('dialog.txt', 'w') as f:
f.write(dialog)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
This challenge was a little interesting because of the use of the columnar cipher, a transposition cipher similar to the Railfence Cipher because of how you manipulate the plaintext. Explaining the entire algorithm is going to take a while because of how many images I’ll have to put up, but I’ll quickly describe it.
- Start by selecting a key that will act as a permutation for our plaintext
- Write the plaintext in a grid/matrix where the number of columns is the length of the key
- Using your key, go to the corresponding column, and read down to get ciphertext
 Credit: link
Credit: link
In this example, our plaintext is “The tomato is a plant in the nightshade family”, and our ciphertext is “TINESAX / EOAHTFX / HTLTHEY / MAIIAIX / TAPNGDL / OSTNHMX” (slashes included to make it easier to understand the breakdown).
For our challenge, we can immediately jump to analyzing the columnar cipher because the PRNG literally does not work. Since \(a = p\), the modulus will always return \(b\), and since we are given the last key, we know all of the keys before it.
What I struggled with for so long was understanding what twistedColumnarEncrypt() was doing because of all of the Python one-liners. After deriving a key (the permutation), we break our plaintext into blocks, but then run transpose(). If you’ve ever taken a Linear Algebra class or have worked with matricies before, you’ll remember that a transpose operation will basically flip the rows and the columns, which is exactly what the function does. The encrypt function then shifts the matrix around by rows, and spits out a ciphertext. I struggled to understand this via looking at the code, so I had to write it out by hand:

So, it’s really not that hard to actually reverse the encryption at all if you know the permutation. The red indicates how you shouldn’t reverse it. You should break it up into blocks of 4 instead of 3 because of the dimensions of the initial setup.
Solution
#!/usr/bin/env python3
def transpose(array):
return [row for row in map(list, zip(*array))]
def flatten(array):
return "".join([i for sub in array for i in sub])
width = 15
inv_derived_key = [11,13,5,8,2,9,14,6,10,4,12,15,1,3,7] # used dcode.fr, but you could do this by hand
with open('encrypted_messages.txt', 'r') as f:
cts = [x.strip() for x in f.readlines()]
for ct in cts:
# Unflatten
blocks = [ct[i:i+7] for i in range(0, len(ct), 7)]
blocks = [list(b) for b in blocks]
# Reverse the mixup
pt = [blocks[inv_derived_key.index(i + 1)][::-1] for i in range(width)]
# Un-transpose
pt = transpose(pt)
# flatten
print(flatten(pt))
The code basically does the reverse of what I showed on the whiteboard. The only big difference is the inclusion of the inv_derived_key, which is just the inverse permutation of the initial key, which we can see by running the deriveKey on the string in dialog.txt. Running the script, we see a long block of text (we love lore ;-;).
kali@transistor:~/ctf/cyber_apocalypse/crypto/crypto_how_the_columns_have_turned$ python3 solve.py
THELOCATIONOFTHECONVOYDANTEISDETERMINEDTOBEONTHETHIRDPLANETAFTERVINYRYOUCANUSELIGHTSPEEDAFTERTHEDELIVERYS
THECARGOISSAFEWENEEDTOMOVEFASTCAUSETHERADARSAREPICKINGUPSUSPICIOUSACTIVITYAROUNDTHETRAJECTORYOFTHEPLANETA
BECAREFULSKOLIWHENYOUARRIVEATTHEPALACEOFSCIONSAYTHECODEPHRASETOGETINHTBTHELCGISVULNERABLEWENEEDTOCHANGEIT
DONTFORGETTOCHANGETHEDARKFUELOFTHESPACESHIPWEDONTWANTANYUNPLEASANTSURPRISESTOHAPPENTHISSERIOUSMISSIONPOPO
IFYOUMESSUPAGAINILLSENDYOUTOTHEANDROIDGRAVEYARDTOSUFFERFROMTHECONSTANTTERMINATIONOFYOURKINDAFINALWARNINGM
Flag: HTB{THELCGISVULNERABLEWENEEDTOCHANGEIT}
Comments